Newton Protocol 作为去中心化基础设施层,用于可验证的链上自动化和安全代理授权,支持协议、DAO 和用户通过可验证的代理执行复杂操作,而无需依赖中心化机器人或链下协调。
用户可以安全地授权代理使用可编程权限代表他们行事,确保操作须经其授权方可执行。通过结合可信执行环境 (TEE)、零知识证明和模块化代理架构,Newton Protocol 实现了完全链上自动化,增强了透明度、可组合性和可信度。
代币用例:
质押以确保协议安全:网络参与者可通过 NEWT dPoS 质押,为 Newton Keystore 汇总的安全性和正常运行做出贡献。
支付 Gas 费/手续费:NEWT 是 Newton Protocol 的原生 Gas 代币,用于发放、更新或撤销指定账户的链上权限(例如,当将账户委托给自主代理时)。
于 Newton 模型注册表使用:代理运营商提供 NEWT 代币作为抵押品,供其自动化服务使用在 Newton Protocol 上运行的注册代理模型。
治理:Newton Protocol 及其生态系统将随着时间的推移而加深去中心化程度,而质押 NEWT 的用户将有权在治理流程中投票,帮助指引 Newton Protocol 的增长和发展。
Newton Protocol 围绕三大核心组件设计:
Newton 模型注册表:规范的链上注册表,用于发布和介绍代理模型(触发行动合约)。
Newton Keystore:专用汇总,负责存储和更新用户权限(例如会话密钥、zkPermissions),这些权限将决定哪些代理可以代表用户行事。
自动化意图:提交给网络的用户定义指令,当满足特定的链上或链下条件时执行操作。
Magic Newton 基金会成立后,从 Magic Labs 获得了 100 万美元的资金,用于资助其近期开支,包括法律费用、运营成本、承包商以及与非关联第三方供应商的合同。该基金会尚未从投资者处筹集任何资金。截至本文件发布时,该基金会尚未进行任何 NEWT 代币的公募或私募。
NEWT 的总供应量为 1,000,000,000 枚,截至 NEWT 代币发布之日,其流通供应量为 215,000,000 枚(占代币总供应量的 21.5%),其中包括分配给空投、验证者奖励和流动性支持的份额。
关键指标(截至 2025 年 6 月 23 日):
1. 什么是 Newton Protocol?
项目概览:
Newton Protocol 是可验证的开放基础设施层,旨在为链上金融带来可编程的安全自动化。在当今的去中心化生态系统中,用户和协议仍然过度依赖链下服务和手动操作来执行关键的金融任务,包括定投、代币分发和金库运营,由此带来了不必要的风险、麻烦和中心化。
为解决这一痛点,Newton Protocol 支持开发人员和协议创建自主链上代理,可用于监控行情、执行预定义操作并协调复杂的金融行为,而无需依赖链下机器人或中介机构。该协议提供了一种标准化方案,将“若这样,则那样”的逻辑直接编码至区块链生态系统中,从而实现金融的去中心化和自主运营。
项目使命:
Magic Newton 基金会的使命在于管理 Newton Protocol 的发展,使其成为加密货币原生金融世界的去信任化自动化层,从而增强整个生态系统的安全性、可扩展性和用户体验。该基金会致力于提升协议和 DAO 的运行效率,同时帮助用户更加自信从容地参与链上市场。
项目价值主张
可验证的代理(无盲目信任)、可编程的权限(细粒度风险控制)和开放的代理市场共同创建了一款即插即用的协调层,可供任何链、DAO 或钱包集成。NEWT 通过安全性质押、Gas 和治理用例,为 Newton Protocol 提供支持。
项目要点:
Newton Protocol 旨在充当链上金融的可验证自动化层。其采用分离意图定义、执行和验证的模块化架构,为发布、验证和执行自动化意图(触发行动程序)提供专用机制。
Newton Protocol 围绕三大核心组件设计:
Newton 模型注册表:规范的链上注册表,用于发布和介绍代理模型(触发行动合约)。
Newton Keystore:专用汇总,负责存储和更新用户权限(例如会话密钥、zkPermissions),这些权限将决定哪些代理可以代表用户行事。
自动化意图:提交给网络的用户定义指令,当满足特定的链上或链下条件时执行操作。
现有产品:

Newton Protocol 作为专用基础设施,致力于实现可验证的 AI 驱动自动化,由自动化护栏、执行证明和代理模型注册表提供支持。

上方所示的网络效应展示了协议参与者的不同角色,他们共同实现了 Newton Protocol 的功能。
NEWT 发布时,首个基于 Newton Protocol 构建的可验证代理演示版也在 newton.xyz 上推出,现已拥有超过 110 万名注册用户、60 万笔已验证代理交易和 35 万个已激活代理。
2. 代币销售与代币经济学:
代币分配:
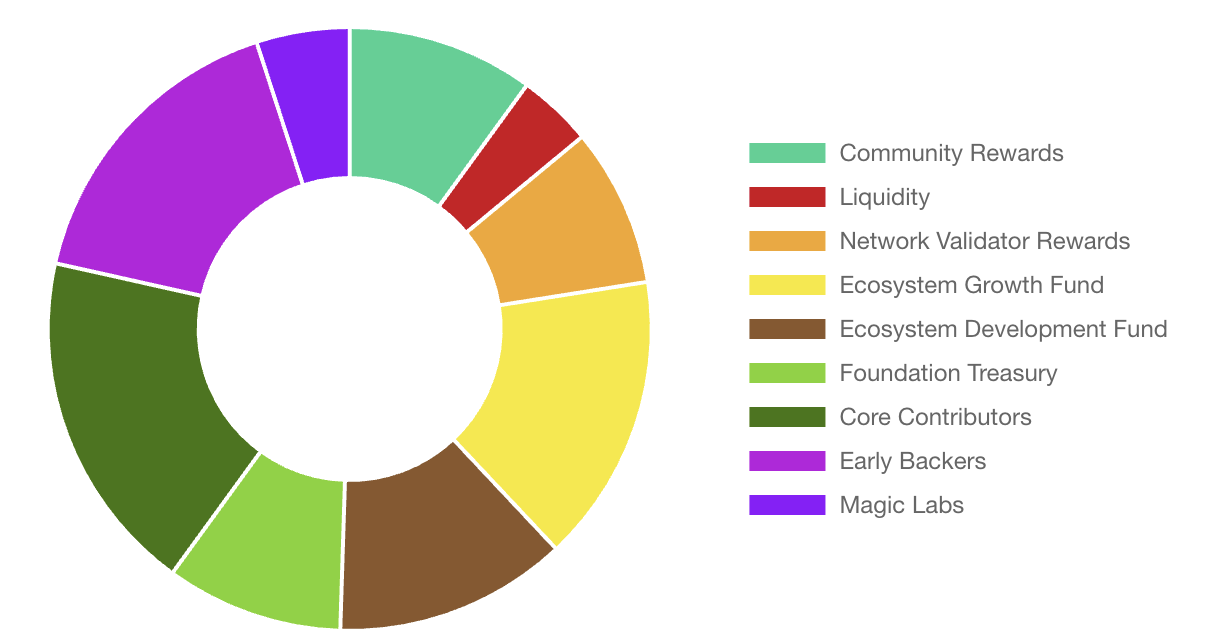
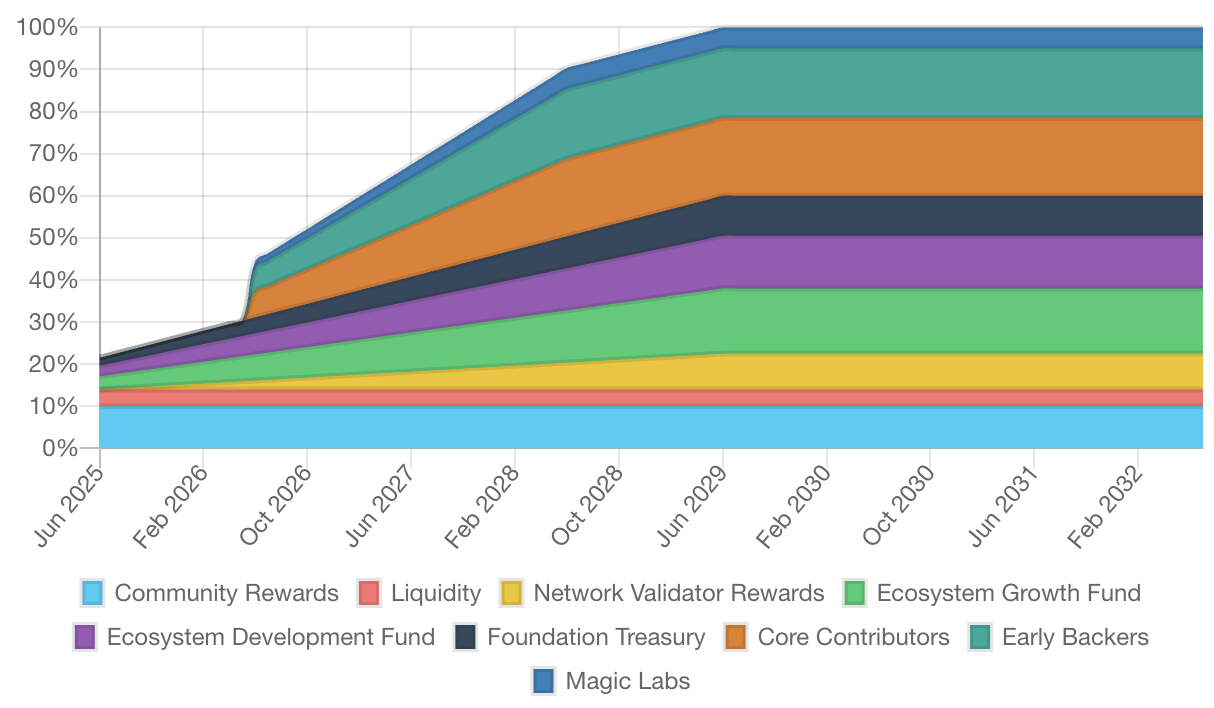
代币释放时间表:
3. 风险分析:
初始流通量散户 : 机构比率:
空投集群分析:
初始 TGE 主分配池链上钱包地址:
其他风险:该项目的某些产品功能仍在开发中,当前效用可能有限。加密货币投资有风险,请务必自己做好研究。
4. 路线图与更新
已完成里程碑:
该协议自创立以来已达成多项重要里程碑,包括:
发布简版技术白皮书(参见 https://blog.newt.foundation/the-litepaper/)
开发可验证自动化协议 V1
将首个上线代理端到端集成至协议中,实现验证自动化
验证基于 TEE(可信执行环境)的代理计算:生成 TEE 认证的零知识证明 (ZKP),并通过协议合约验证其可靠性
由 Magic Labs 开发的定投代理,允许用户通过可验证的自动化工具,安排资产定投
在协议上质押 NEWT 代币
多项社区奖励计划
建立基金会和治理路线图,以支持协议开发和生态系统增长的中立管理
展望未来,Newton Protocol 将继续遵循以下主要发展方向:
可验证的自动化市场
推出由 Newton 模型注册表提供支持的链上市场,使任何人都可以轻松发布、发现并组合代理或代理 Swarm(即多个代理组成的复杂协作团队)。此举可解锁更多自动化策略和用例,同时培育充满活力的可组合代理生态系统,供终端用户直接交互。多链 Newton Keystore 汇总
推出 zkPermissions 汇总,实现经济高效、兼容多链的零知识权限。开发人员可自行定义可编程护栏,例如“仅当波动性超过 X 时进行交易”或“仅当 RSI 低于 Y 时采取行动”,并使用 SDK 简化 zkPermission 与代理的集成。可扩展性
通过聚合证明验证等技术提高可扩展性。此类升级可降低成本并提高吞吐量,使得高频率、可验证的自动化在大规模应用中具有经济可行性。去中心化
通过引入第三方验证者逐步实现协议的去中心化,保障 Newton Keystore 汇总的安全性。此举增强了抗审查性,并确保验证机制随着时间的推移始终保持可靠中立和去信任化。
白皮书链接:https://blog.newt.foundation/the-litepaper/
商业及业务发展进展:
Newton Protocol 融合多项开源和第三方组件,对其功能至关重要。其中包括:
可信执行环境 (TEE):用于证明代理执行的可靠性。该协议目前利用 Phala 的云环境,以去中心化的可验证方式运行机密计算任务。若条件允许,还可添加额外的云环境和冗余。
零知识证明系统:Newton 支持基于零知识的授权和证明生成,作为其权限模型和代理验证的一部分。该协议与新兴的 zk-VM 框架(如 Succinct 和 Risc Zero)集成,实现可验证的链下计算和可扩展的加密证明。
zk-SNARKs 和权限库:用于构建并验证精细化访问控制(例如,zkPermissions 和会话密钥),确保只有获得授权的代理才能代表用户执行自动化操作。
以太坊 Layer 1 和 Layer 2 生态系统:Newton Protocol 将最终性证明和授权状态根发布到以太坊上,旨在实现与其他链的跨链互操作性。
该协议在适用条件下构建于经过实践检验的开源库之上,并尽可能将自身改进向上游反馈。
5.社区
X:https://x.com/newtfoundation
6. 附录:
敬请参阅 https://newt.foundation/ 上发布的披露和透明度报告,了解更多有关该项目的信息。
